Employment opportunities for community health workers are better than ever. Organizations like the Centers for Disease Control and the US Department of Health & Human Services are frequently announcing new programs, funding and resources for CHWs in an effort to improve health outcomes and reduce the cost of hospitalization and long-term conditions in the health system. It’s no wonder why more organizations are looking for ways to include CHWs and provide more CHW core competency training for internal staff. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects continued growth for the CHW career between 2020 and 2030 — so now is a great time to uplevel your core skills and put yourself on a CHW career path while improving health outcomes for your community.
→ Enroll Now: CHW Core Competencies Online Training [Certificate]
Careful planning of a CHW career path can allow anyone who starts with an entry-level job to expand it into a rewarding career. As the need for this role keeps growing, CHWs can not only increase the health knowledge of their community members but also increase their own reach to more people and other job opportunities.
CHW Job Outlook
The statistics are inspiring. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, jobs for CHWs are expected to rise by 18.1% by 2026. That means that 10,400 jobs could open up. Also, salaries for already employed CHWs are increasing. Wages are good, about $23.49 per hour, or $48,860 per year.
Developing the skills to become a CHW can open the door to a money-making and secure career.
Building a CHW career path — rather than just finding an entry-level job — involves understanding the core competencies and what kinds of skills are useful for growth into the future.
In order to earn a profitable job and build a lasting career, current CHWs and people who would like to be one need to keep their health and professional skills sharp. They need to take extra training and prove their knowledge and expertise through certification.
CHWTraining’s Core Competencies Training offers complete, up-to-date training for employers who want to provide staff with foundational skills and knowledge of specific health topics, such as diabetes or breast cancer.
We created the quick guide below as a tool for employers who want to build sustainable training programs and CHWs who want to understand the job qualifications.
CHW Core Skills
CHWs are employed in every state of the US (except South Dakota, for which no data is available), according to the BLS. Each state has independent job requirements, which vary from college degrees that take multiple years to complete to on-the-job training. Some states require certification, and some employers require certificates of completion to show successful core skills training.
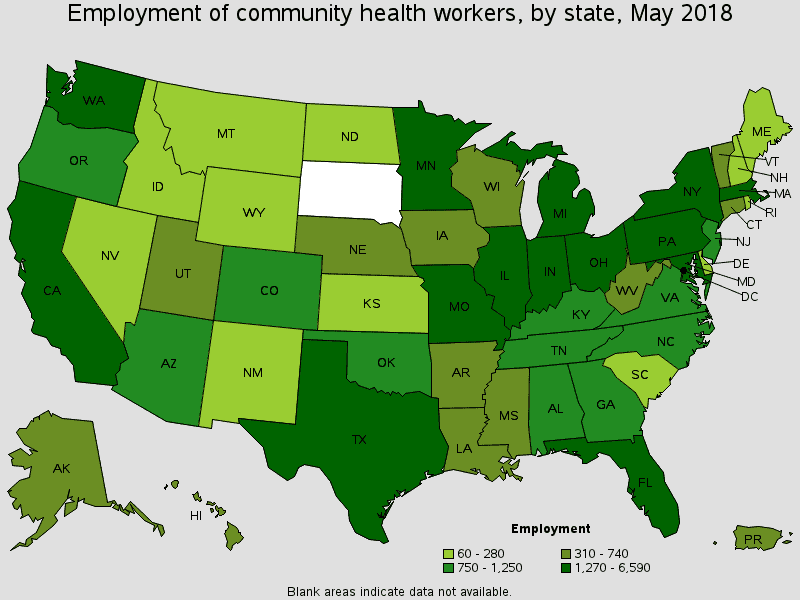
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
However, many core skills training requirements are similar. The following are common skills required by many programs and advisory committees. Here are some CHW core competency training areas common among the Washington State Department of Health’s CHW program, the Roles and Competencies from the Community Health Worker Core Consensus (C3) Project, the US Department of Labor Employment & Training Administration, and the Massachusetts Department of Public Health. You can compare more national requirements at State Community Health Worker Models from the National Academy for State Health Policy (NASHP) or from this guide.
15 Most Important Core Skills To Build a CHW Career Path
| CHW Core Competency | Example Skills |
| Advocacy Skills/Capacity Building Skills | Empowering clients Motivating people to manage their own health and advocate for themselves Helping clients and patients set and reach their goals Supporting behavior change Identifying and overcome barriers Understanding community cultures and ways to reach members |
| Care Coordination or Service Coordination and System Navigation | Navigating systems Collaborating with partners to connect clients and patients to resources Helping service providers work together Telling systems about needs of people Helping to develop and implement care plans |
| Communication Skills | Listening skillsLanguage skills Building rapport Using nonverbal communication Resolving and avoiding conflict Understanding and working within culturally diverse communities |
| Cultural Humility/Cultural Responsiveness | Serve as a bridge between different cultures Translating healthy behaviors into culturally appropriate equivalents Understanding and working to reduce health disparities Using cultural sensitivities for all diverse groups Behaving respectfullyIdentifying biases |
| Education and Facilitation Skills | Using various ways to deliver health information clearly Explaining terms in plain language Promoting healthy behavior change Finding and use resources to develop self-efficacy skills |
| Evaluation and Research | Identifying issues in communities and their causes Conducting evaluation projects Collecting data Sharing results Communicating to stakeholders to make changes in services |
| Experience and Knowledge Base | Fully understanding the community, including social determinants of health, health issues, ways to improve health and self-care, and basic public-health principles Understanding how US social-service systems work |
| Individual and Community Assessment and Direct Services | Identifying needs, strengths and resources of communities Helping meet needs Helping clients understand their needs and overcome barriers Providing social and health support |
| Interpersonal and Relationship-Building Skills | Establishing trust with people and in communities Being open-minded Using Motivational Interviewing techniques |
| Outreach Skills, Methods and Strategies | Developing and implementing outreach plans Sharing information about programs and resources Creating and maintain relationships with community members and partners |
| Healthy Eating Active Living (HEAL) Promotion | Educate clients about the benefits of self-case, physical activity and healthy eating Teach clients about how healthy lifestyle habits can help manage or prevent chronic illness Overcome barriers like food insecurity for healthy choices |
| Service Coordination and Navigation Skills | Coordinate service for clients and those in internal and external networks Make referrals Track clients’ progress and follow up Help clients follow their care plan |
| Organizational and Documentation Skills | Break down complex topics to make them manageable for clients Research and collect health information from and for community members and clients Bring accurate, relevant health information according to cultural contexts |
| Professional Skills and Conduct | Develop time management skills Set goals and clear action plans to achieve them Set clear boundaries with clients and coworkers Follow ethical standards like codes of ethics, laws, and institutional guidelines |
| Public Health | Understand the public health structure Understand CHWs’ role within the healthcare system at large Identify the challenges and opportunities in a community by addressing the four pillars of public health Apply a combination of theoretical knowledge and culturally relevant experience to understand public health on a local scale |
Originally published Oct 31, 2019, updated May 17, 2022.
Core Competencies for CHWs
Register now for this foundational course and save with the Early Bird Discount.

